What's a resource?
Resources are the tools and services you use to make assets. Let’s go back to our example about cookies to help contextualize this.
Multiple kitchen utensils and appliances are used when baking. When making cookies, you’ll need a bowl and spoon to hold and mix ingredients, a tray to put the cookies on, and an oven to bake them. These can be considered resources.
If we add these resources to our kitchen, our cookie pipeline would look like this:
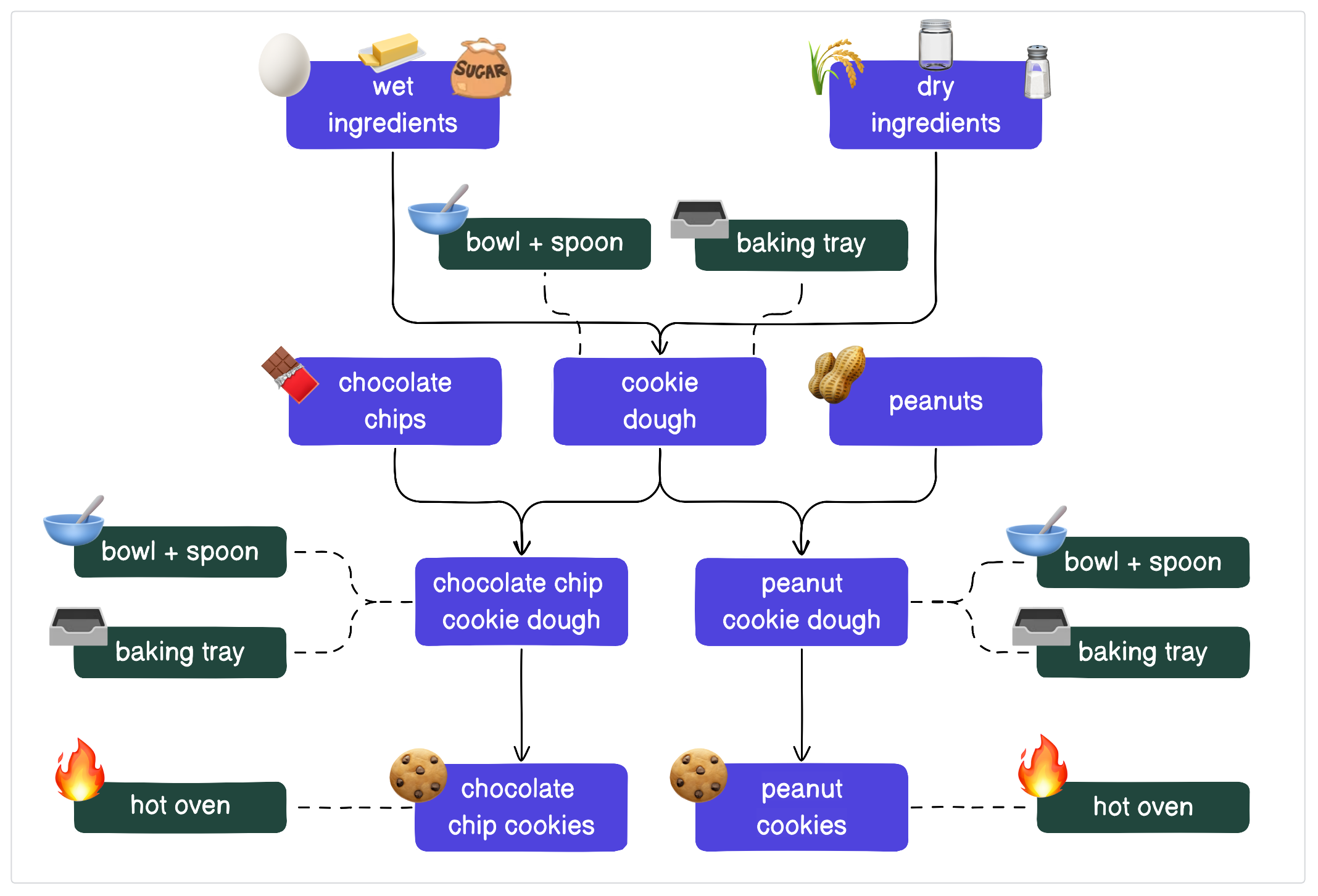
In this case, the bowl and spoon, baking tray, and oven are used multiple times by different assets. Not only is it difficult to answer how many times you need a baking tray or which assets need an oven, it’s repetitive. Instead of needing multiples of these resources, we can have one of each and re-use them.
If we alter our approach to be more DRY we can simplify our pipeline and centralize our configurations. To do this, we’ll define the resources in one place and add references where they’re used:
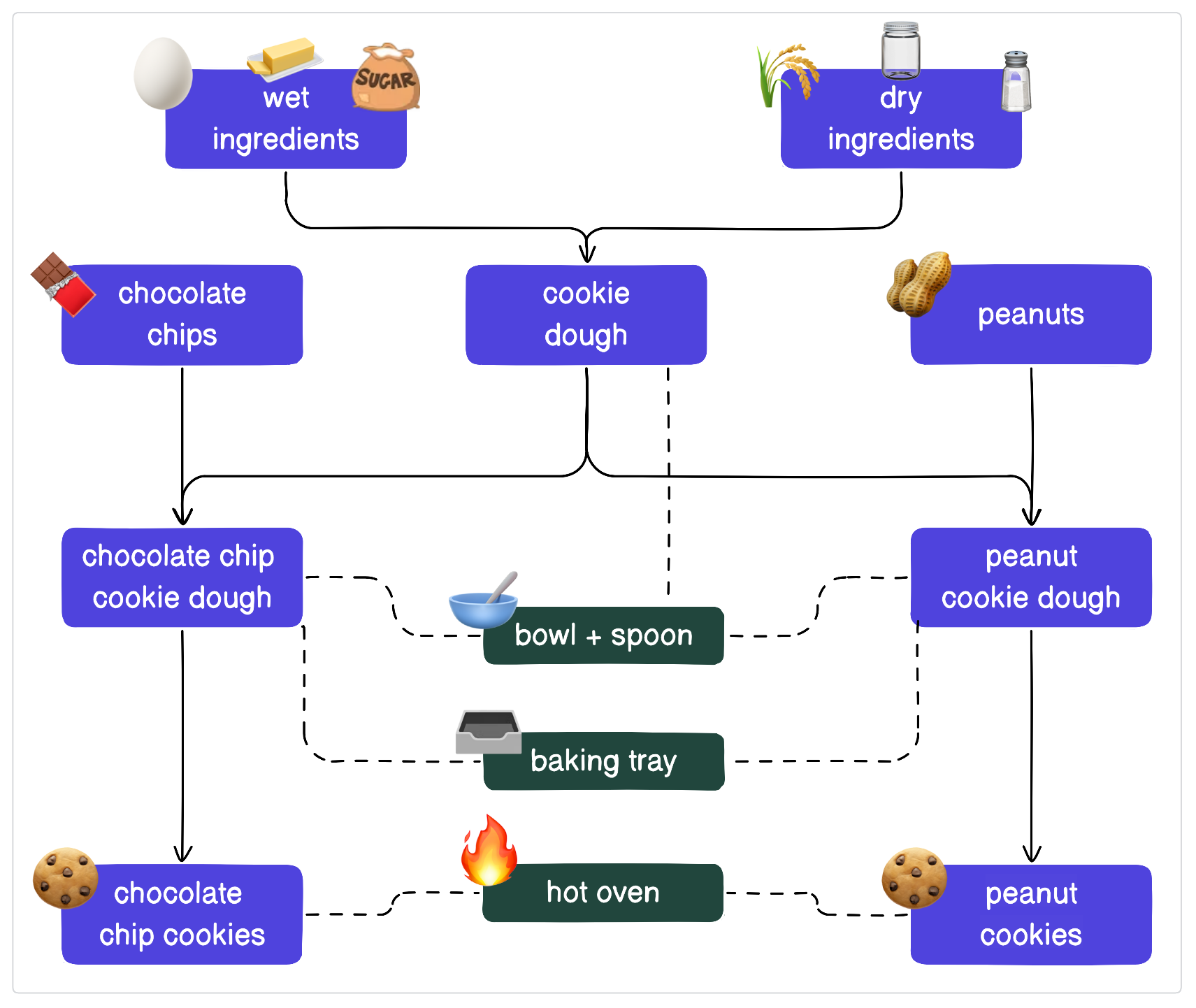
Resources in Dagster
Much like baking, making data pipelines also requires resources. For example, a simple ETL (Extract Transform Load) pipeline fetches data from an API, ingests it into a database, and updates a dashboard. External tools and services this pipeline uses could be:
- The API the data is fetched from
- The AWS S3 bucket where the API’s response is stored
- The Snowflake/Databricks/BigQuery account the data is ingested into
- The BI tool the dashboard was made in
All of the above are resources. In data engineering, resources are the external services, tools, and storage you use to do your job. A data orchestrator should be aware of the different tools used, where they’re used, and how they’re used.
With this in mind, Dagster resources promote standardizing your connections and integrations to these tools. The Dagster UI also details where and how resources are used and configured.
In this lesson, you’ll lightly refactor the project you have so far to manage your DuckDB connections with a resource.