Connecting dbt models to Dagster assets
With where we left off, you may have noticed that the sources for your dbt projects are not just tables that exist in DuckDB, but also assets that Dagster created. However, the staging models (stg_trips, stg_zones) that use those sources aren’t linked to the Dagster assets (taxi_trips, taxi_zones) that produced them:
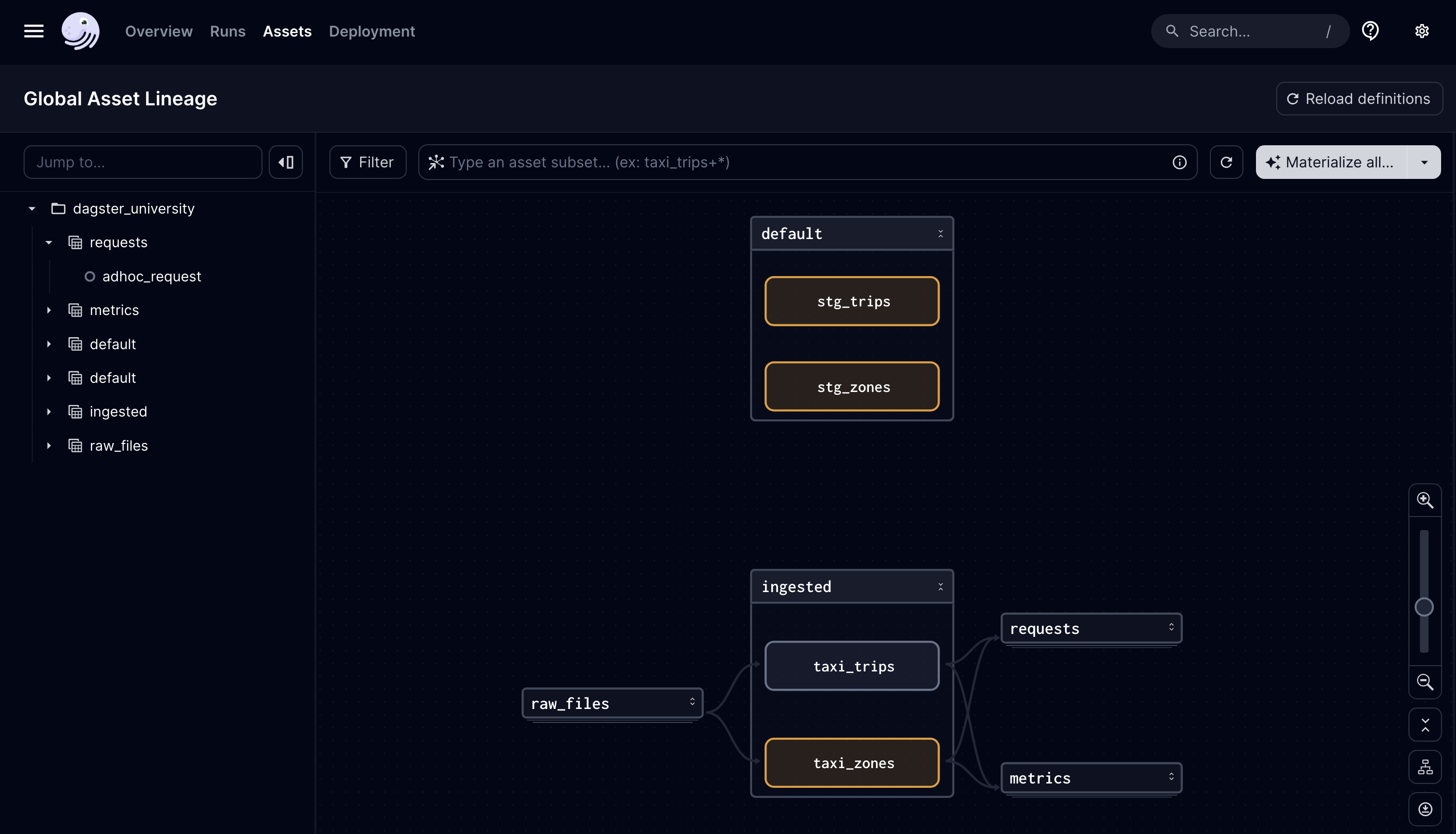
Let’s fix that by telling Dagster that the dbt sources are the tables that the taxi_trips and taxi_zones asset definitions produce. To match up these assets, we'll override the dbt assets' keys. By having the asset keys line up, Dagster will know that these assets are the same and should merge them.
This is accomplished by changing the dbt source’s asset keys to be the same as the matching assets that Dagster makes. In this case, the dbt source’s default asset key is raw_taxis/trips, and the table that we’re making with Dagster has an asset key of taxi_trips.
To adjust how Dagster names the asset keys for your project’s dbt models, we’ll need to override the dagster-dbt integration’s default logic for how to interpret the dbt project. This mapping is contained in the DagsterDbtTranslator class.
Customizing how Dagster understands dbt projects
The DagsterDbtTranslator class is the default mapping for how Dagster interprets and maps your dbt project. As Dagster loops through each of your dbt models, it will execute each of the translator’s functions and use the return value to configure your new Dagster asset.
However, you can override its methods by making a new class that inherits from and provides your logic for a dbt model. Refer to the dagster-dbt package’s API Reference for more info on the different functions you can override in the DagsterDbtTranslator class.
For now, we’ll customize how asset keys are defined by overriding the translator’s get_asset_key method.
Open the defs/assets/dbt.py file and do the following:
Update the imports to include:
- From the
dagster_dbtmodule, importDagsterDbtTranslator - From the
dagstermodule, importAssetKey
- From the
Create a new class called
CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslatorthat inherits from theDagsterDbtTranslator. Add this code after the imports inassets/dbt.py:class CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator(DagsterDbtTranslator):In this class, create a method called
get_asset_key.This is a method of the
DagsterDbtTranslatorclass that we'll override and customize to do as we need. It is an instance method, so we'll have its first argument beself, to follow Pythonic conventions. The second argument refers to a dictionary/JSON object for the dbt model’s properties, which is based on the manifest file from earlier. Let’s call that second argumentdbt_resource_props. The return value of this function is an object of theAssetKeyclass.class CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator(DagsterDbtTranslator): def get_asset_key(self, dbt_resource_props):Now, let’s fill in the
get_asset_keymethod with our own logic for defining asset keys.There are two properties that we’ll want from
dbt_resource_props: theresource_type(ex., model, source, seed, snapshot) and thename, such astripsorstg_trips. Access both of those properties from thedbt_resource_propsargument and store them in their own respective variables (typeandname):def get_asset_key(self, dbt_resource_props): resource_type = dbt_resource_props["resource_type"] name = dbt_resource_props["name"]As mentioned above, the asset keys of our existing Dagster assets used by our dbt project are named
taxi_tripsandtaxi_zones. If you were to print out thename, you’d see that the dbt sources are namedtripsandzones. Therefore, to match our asset keys up, we can prefix our keys with the stringtaxi_.Copy and paste the following code to return an
AssetKeyofAssetKey(f"taxi_{name}"):def get_asset_key(self, dbt_resource_props): resource_type = dbt_resource_props["resource_type"] name = dbt_resource_props["name"] return dg.AssetKey(f"taxi_{name}")You have full control over how each asset can be named, as you can define how asset keys are created. In our case we only want to rename the dbt sources, but we can keep the asset keys of the models the same.
The object-oriented pattern of the
DagsterDbtTranslatormeans that we can leverage the existing implementations of the parent class by using thesupermethod. We’ll use this pattern to customize how the sources are defined but default to the original logic for deciding the model asset keys. Copy and paste the code below to complete theget_asset_keyfunction:def get_asset_key(self, dbt_resource_props): resource_type = dbt_resource_props["resource_type"] name = dbt_resource_props["name"] if resource_type == "source": return dg.AssetKey(f"taxi_{name}") else: return super().get_asset_key(dbt_resource_props)You’ve successfully written your first translator!
💡 Important! dbt models and Dagster asset keys must be unique. If you're receiving a
DuplicateKeyError, add some logging to verify that the logic inget_asset_keydoesn't return two of the same key for different values!
Now, update the definition that uses
@dbt_assetsto be configured with an instance of theCustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator. The@dbt_assetsdecorator has adagster_dbt_translatorargument that you can pass this instance into. Don’t forget to instantiate the class!Your code should look something like this:
@dbt_assets( manifest=dbt_project.manifest_path, dagster_dbt_translator=CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator() ) def dbt_analytics(context: dg.AssetExecutionContext, dbt: DbtCliResource): yield from dbt.cli(["build"], context=context).stream()
At this point, your defs/assets/dbt.py file should match the following:
# src/dagster_and_dbt/defs/assets/dbt.py
import dagster as dg
from dagster_dbt import DagsterDbtTranslator, DbtCliResource, dbt_assets
from dagster_and_dbt.defs.project import dbt_project
class CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator(DagsterDbtTranslator):
def get_asset_key(self, dbt_resource_props):
resource_type = dbt_resource_props["resource_type"]
name = dbt_resource_props["name"]
if resource_type == "source":
return dg.AssetKey(f"taxi_{name}")
else:
return super().get_asset_key(dbt_resource_props)
@dbt_assets(
manifest=dbt_project.manifest_path,
dagster_dbt_translator=CustomizedDagsterDbtTranslator(),
)
def dbt_analytics(context: dg.AssetExecutionContext, dbt: DbtCliResource):
yield from dbt.cli(["build"], context=context).stream()